
QD-OLED: Quantum Dot Organic Light Emitting Diode
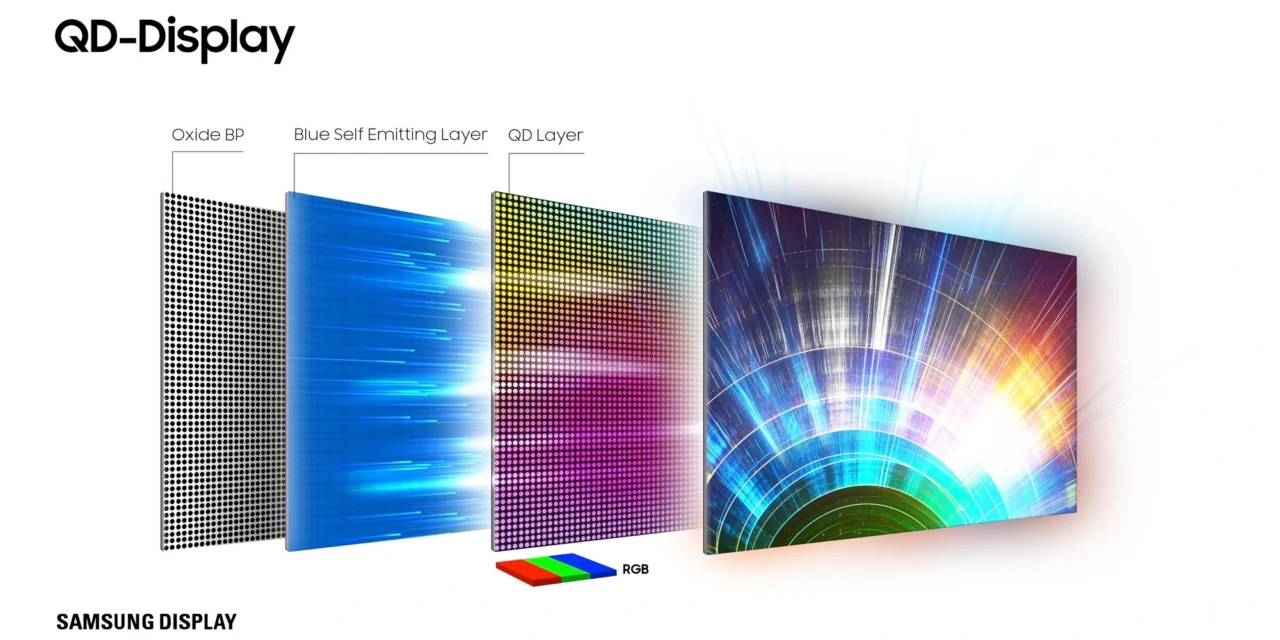
Quantum Dot Organic Light Emitting Diode (QD-OLED) is a display technology that combines the best of two worlds: the brightness and color accuracy of Quantum Dot (QD) displays, and the contrast and power efficiency of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs). QD-OLED is a relatively new technology that is being developed by several companies, including Samsung and TCL. In this article, we’ll explore what QD-OLED is, how it works, and what its potential advantages are.
Table of Contents
What is QD-OLED?
QD-OLED is a display technology that uses a combination of Quantum Dots and Organic Light Emitting Diodes to produce images on a screen. Quantum Dots are tiny crystals that emit light of a specific color when exposed to light or electricity. OLEDs, on the other hand, are made up of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is passed through them. By combining the two technologies, QD-OLED aims to produce a display that is brighter, more color accurate, and more energy-efficient than either technology on its own.
The development of QD-OLED began in the early 2010s, with the first patents filed by Samsung in 2013. Since then, several companies have been working on developing the technology, including Samsung, TCL, and JOLED. Samsung’s QD-OLED technology is called QD-Display, while TCL’s is called H-QLED. JOLED has also developed its own QD-OLED technology, which it calls Printed OLED.
How does QD-OLED work?
QD-OLED works by using a layer of Quantum Dots to convert blue light from the OLED into red and green light. This layer of Quantum Dots is placed between the OLED layer and the color filter layer. The OLED layer produces blue light, which is then converted by the Quantum Dots into red and green light. The color filter layer then separates the red, green, and blue light to produce a full-color image.
One of the key advantages of QD-OLED is that it can produce incredibly accurate colors, thanks to the precise control over the Quantum Dots. Quantum Dots can be tuned to emit light at very specific wavelengths, allowing for a much wider range of colors than traditional LED displays. This means that QD-OLED displays can produce colors that are much more vivid and lifelike than other display technologies.
Another advantage of QD-OLED is that it can produce incredibly bright images, thanks to the high brightness of the blue OLED layer. Because the Quantum Dots are converting the blue light into red and green light, there is less light loss than in traditional OLED displays, allowing for brighter images.
What are the potential advantages and challenges of QD-OLED?
QD-OLED has several potential advantages over other display technologies, including:
- Better color accuracy: QD-OLED can produce incredibly accurate colors, thanks to the precise control over the Quantum Dots. This means that images can look more lifelike and vivid than on other display technologies.
- Brighter images: QD-OLED can produce brighter images than traditional OLED displays, thanks to the high brightness of the blue OLED layer and the less light loss from the Quantum Dot conversion.
- Improved energy efficiency: QD-OLED can be more energy-efficient than traditional OLED displays, thanks to the reduced light loss from the Quantum Dot conversion.
- Longer lifespan: QD-OLED displays may have a longer lifespan than traditional OLED displays, thanks to the reduced stress on the blue OLED layer.
- Lower manufacturing costs: QD-OLED may be cheaper to manufacture than traditional OLED displays, thanks to the simpler manufacturing process and the reduced need for color filters.
Here are some of the challenges that QD-OLED needs to overcome:
Manufacturing complexity: One of the challenges of QD-OLED is the manufacturing complexity involved in producing the Quantum Dot layer. The Quantum Dot layer needs to be very precise and uniform in order to produce accurate colors, and this requires a complex manufacturing process. This complexity can lead to higher manufacturing costs and lower production yields, which can make QD-OLED displays more expensive than other display technologies.
- Manufacturing complexity: One of the challenges of QD-OLED is the manufacturing complexity involved in producing the Quantum Dot layer. The Quantum Dot layer needs to be very precise and uniform in order to produce accurate colors, and this requires a complex manufacturing process. This complexity can lead to higher manufacturing costs and lower production yields, which can make QD-OLED displays more expensive than other display technologies.
- Stability issues: Another challenge of QD-OLED is stability issues, particularly with regards to the Quantum Dot layer. Quantum Dots can degrade over time, leading to changes in color accuracy and brightness. This can lead to a shorter lifespan for QD-OLED displays and reduced image quality over time.
- Color filter issues: QD-OLED uses a color filter layer to separate the red, green, and blue light produced by the Quantum Dots and the OLED layer. However, this color filter layer can reduce the brightness of the display and also introduce color inaccuracies. This can affect the color accuracy and brightness of the final image, and needs to be addressed in order to improve the performance of QD-OLED displays.
- Patent issues: QD-OLED is a technology that is being developed by several companies, each with its own patents and intellectual property. This can lead to legal disputes and barriers to the adoption of the technology, particularly if companies are unable to agree on licensing terms.
- Competition from other display technologies: QD-OLED faces competition from other display technologies, including OLED, QLED, and MicroLED. Each of these technologies has its own advantages and challenges, and QD-OLED needs to demonstrate that it can offer significant advantages over these other technologies in order to gain market share.
Conclusion
QD-OLED is a promising new display technology that combines the best of Quantum Dots and Organic Light Emitting Diodes to produce bright, color-accurate, and energy-efficient displays. QD-OLED has several potential advantages over other display technologies, including better color accuracy, brighter images, improved energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and lower manufacturing costs. However, QD-OLED also faces several challenges, including manufacturing complexity, stability issues, color filter issues, patent issues, and competition from other display technologies. Despite these challenges, QD-OLED has the potential to revolutionize the display industry, and we can expect to see more QD-OLED products hitting the market in the coming years as the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted.































